Visual Navigation
As usual, we start with our ls binary.
$ r2 -A /bin/ls
[0x004048c5]>
We can enter visual mode with the command V.
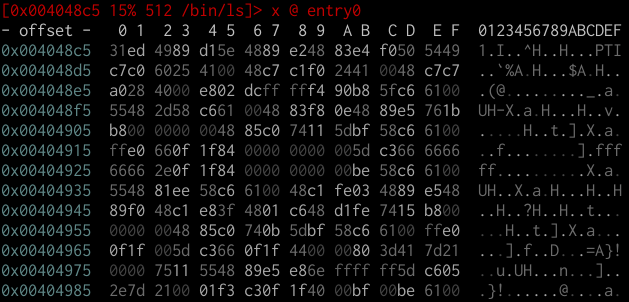
You will be presented with a hex view of the binary. You can cycle between view modes using p and P. You can identify each mode by reading the prompt, which shows you which command is being run to generate the output.
[0x004048c5 15% 512 /bin/ls]> x @ entry0 # Hex mode
[0x004048c5 15% 512 /bin/ls]> pd $r @ entry0 # Disassembly mode
[0x004048c5 15% 160 /bin/ls]> ?0;f tmp;s.. @ entry0 # Hex|Registers|Disassembly
[0x004048c5 15% 512 /bin/ls]> pxw @ entry0 # Hex words
[0x004048c5 15% 160 /bin/ls]> pc @ entry0 # C buffers
[0x004048c5 15% 4096 /bin/ls]> pxA @ entry0 # Operation analysis
[0x004048c5 15% 512 /bin/ls]> pxa @ entry0 # Annotated hexdump
For now, we are going to focus on the disassembly view (by pressing p once).

Getting help
As always, you can press ? to view available shortcuts in this mode. For now, we will focus on navigation; there are a few shortcuts which are not so obvious.
Basic movement
You can move up or down (instruction by instruction) via the arrow keys or j (down) and k (up), similar to Vim. Move up or down over entire functions via n and N.
When the current instruction is a jmp or a call, you can follow it by pressing <Enter>. But there's a faster way. Notice that the call sym.imp.__libc_start_main instruction has a comment with the number 1 between square brackets. If you press 1, even if you are not currently positioned on the call instruction, you will follow that call. The same goes for the jmp instruction further down, with 2 commented in square brackets.
You can go to any offset with o. You can undo any seek at any time via the u key and redo it with U.
Marks
You can set marks at any point using m followed by any key (case-sensitive). To go to a mark, press ' followed by the mark key. Be aware that marks are not highlighted in any way in contrast to flags.
Fuzzy flag searcher
A fuzzy-like searcher can be accessed with the _ key, very handy for quickly finding and switching between functions, strings and other flags.
Cross-references
You can get a list of cross-references (xrefs, for short) from/to data using x and X, respectively.
For example, pressing X in main will yield
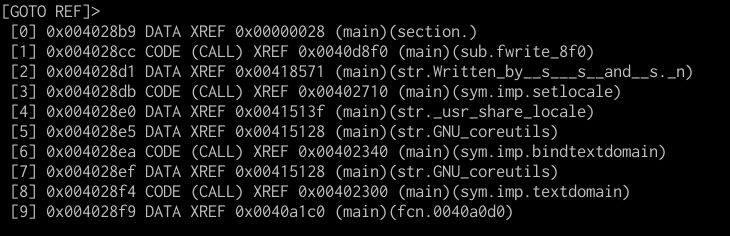
Again, using the numbers 1-9, you can quickly go to any of these references.